
High Carbon Steel Billet vs Billet Stainless Steel: Top 3 Secrets
Table of Contents
Introduction
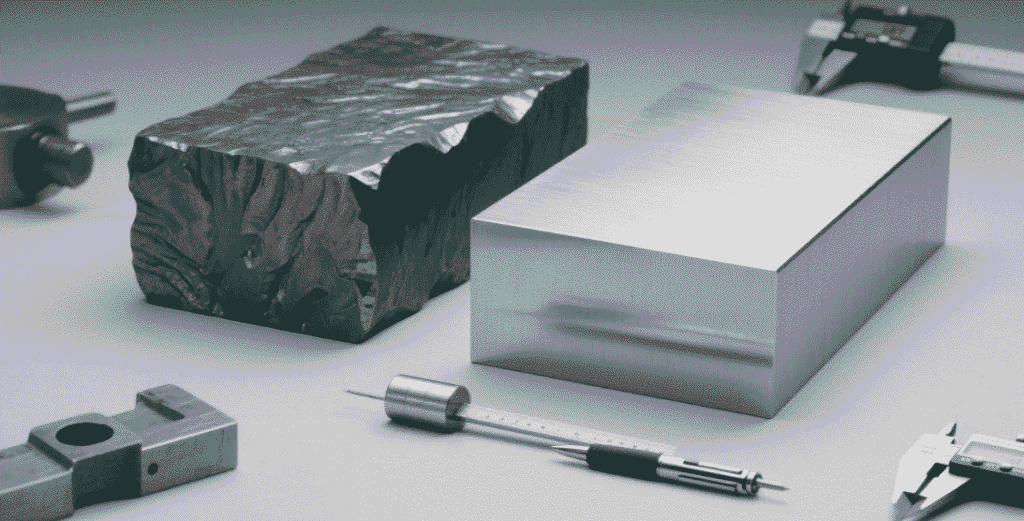
In the intricate world of manufacturing and construction, the foundational choice of raw materials dictates the integrity, performance, and longevity of the final product. For B2B buyers, particularly those in sectors reliant on robust metal components, the selection of the appropriate steel billet is a decision laden with critical implications. Our sources underscore this by highlighting that “Why Steel Grade Selection is Crucial for Product Quality”.
This principle is especially true when contemplating two common yet fundamentally different options: high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel. Both offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, making an informed decision paramount. Companies like Henan Jiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., established in 1958 and known for producing high-quality steel bars and steel billet products, emphasize this by providing extensive technical support and a range of processing services to ensure clients choose correctly.
This blog post aims to demystify the choices between high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel by unveiling three top secrets that every B2B buyer should understand. We will delve into their definitions, compare their performance attributes, explore their ideal application scenarios, and discuss the critical role of quality standards and supplier expertise in procurement. Understanding these nuances will not only safeguard your investment but also enhance the quality and reliability of your end products.
Understanding Your Options: What is high carbon steel billet?
A high carbon steel billet is a semi-finished long steel product, typically square or rectangular in cross-section, which is subsequently rolled into other forms such as bars or wire rods. What defines a high carbon steel billet is its elevated carbon content, generally ranging from about 0.60% to 1.70% by weight.
This significant carbon presence is the “secret” behind its exceptional hardness and strength, making it ideal for applications requiring severe wear resistance and structural rigidity. The elevated carbon content allows for effective heat treatment optimization, which is a crucial process for enhancing the performance of high carbon steel billet. Through processes like hardening and tempering, the high carbon steel billet can achieve extreme hardness, making it a go-to material for tools, springs, and wear-resistant components.
The high carbon content, while imparting superior hardness and strength, also makes the material less ductile and more brittle compared to lower carbon steels or stainless steels. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration during fabrication, especially in welding and forming operations, which our sources touch upon regarding carbon steel and welding. However, for applications where the “secret” to success lies in durability under abrasive conditions or the need for a rigid structure, high carbon steel billet is often the unparalleled choice. Companies like Jiyuan Steel produce high-quality steel bars, which are often derived from carefully selected steel billet, highlighting the importance of the initial billet quality.
Understanding Your Options: What is billet stainless steel?
In contrast to its high-carbon counterpart, billet stainless steel is defined by its chromium content, typically a minimum of 10.5% by mass. This chromium forms a passive layer on the surface, which is the “secret” to its superior corrosion resistance – a property that high carbon steel billet inherently lacks. This protective layer continuously reforms when exposed to oxygen, effectively preventing rust and staining. Billet stainless steel is also a semi-finished product, similar in form to a high carbon steel billet, destined for further processing into bars, sheets, or tubes.
Beyond corrosion resistance, billet stainless steel offers a range of properties depending on its specific alloy composition and grade. There are numerous grades, such as austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, and precipitation-hardening stainless steels, each offering a unique combination of strength, ductility, weldability, and heat resistance.
This diversity allows B2B buyers to select the “secret” optimal billet stainless steel grade for highly specific applications, from food-grade equipment and medical instruments to architectural elements and chemical processing plants. While often associated with a higher initial cost compared to high carbon steel billet, the long-term benefits of billet stainless steel—suchs as reduced maintenance, extended service life, and hygienic properties—often justify the investment, especially in environments where corrosion or hygiene is a primary concern.
Unveiling the Top 3 Secrets of high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel

The decision between high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel is a multifaceted one, influenced by performance requirements, application environments, and economic considerations. Here, we delve into the three paramount “secrets” that guide this critical material selection process.
Secret 1: Performance Differences – Strength, Hardness, and Corrosion Resistance in high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel
The first secret lies in understanding the fundamental performance disparities. When considering high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel, their mechanical and chemical properties diverge significantly.
• Strength and Hardness: High carbon steel billet generally exhibits superior hardness and tensile strength, especially after appropriate heat treatment. The increased carbon content forms carbides within the steel matrix, which resist deformation and wear. This makes high carbon steel billet an ideal candidate for applications requiring extreme wear resistance and structural integrity under heavy loads, such as in the manufacturing of robust tools, springs, and machine components. The inherent strength of a high carbon steel billet is a key advantage for these demanding uses.
• Corrosion Resistance: This is where billet stainless steel undeniably shines. Its defining characteristic is its exceptional resistance to corrosion, rust, and staining, thanks to its chromium content. For applications exposed to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments, the use of billet stainless steel is not just a preference but often a necessity to ensure the longevity and reliability of the product. High carbon steel billet, lacking this chromium protection, is highly susceptible to rust and requires protective coatings or constant maintenance to prevent degradation, illustrating a major differentiating factor when comparing high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel.
• Toughness and Ductility: While high carbon steel billet is hard and strong, it can be more brittle. Billet stainless steel, particularly austenitic grades, often offers better ductility and toughness, making it more amenable to forming and fabrication without cracking. This balance of properties is crucial for components that might experience impact or require significant bending during manufacturing or service.
Understanding these intrinsic performance differences is the first critical step in correctly differentiating high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel for any specific project.
Secret 2: Application Suitability and Cost Implications for high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel
The second secret involves aligning material properties with specific application requirements and carefully evaluating the total cost of ownership.
• Tailoring to Application: The “secret” to choosing between high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel often lies in the end-use environment. For instance, high carbon steel billet is indispensable in the creation of cutting tools, dies, and railway components where extreme hardness and resistance to abrasion are paramount. Its use in heavy machinery parts capitalizes on its ability to withstand significant mechanical stress. Conversely, billet stainless steel is the preferred choice for environments requiring hygiene, aesthetics, or chemical inertness, such as in food processing equipment, surgical instruments, marine applications, and architectural façades. The “food-grade application” for billet stainless steel ensures sanitation and safety [see previous subheading].
• Cost-Benefit Analysis: While the initial procurement cost of billet stainless steel is generally higher than that of high carbon steel billet, this should not be the sole determinant. The higher cost of billet stainless steel is offset by its extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, and superior performance in corrosive environments.
For a high carbon steel billet, while initially cheaper, the need for protective coatings (like painting or galvanizing) and potential for premature failure in unsuited environments can lead to higher lifetime costs. B2B buyers must conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis considering installation, maintenance, expected lifespan, and the potential costs associated with material failure. This holistic view is crucial when evaluating the long-term value of high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel.
Secret 3: The Imperative of Quality Standards and Supplier Expertise in high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel Procurement
The third, often overlooked “secret,” is the critical role of stringent quality standards and the expertise of your steel supplier. The inherent properties of high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel can only be fully realized if the materials themselves are of high quality and consistency.
• Identifying High-Quality Billets: B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to strict international quality standards. For high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel, this means precise control over chemical composition, microstructure, surface finish, and freedom from internal defects. Our sources highlight the importance of “Inspection Services” and “Tech Support” offered by companies like Jiyuan, which are vital for identifying quality billets and ensuring they meet specifications. A “B2B buyer guide to identifying high-quality steel billets” would emphasize robust quality control processes including chemical analysis and mechanical testing.
• Supplier Expertise: The complexity of steel alloys and their applications necessitates working with suppliers who possess deep technical knowledge. Jiyuan Steel, with its “3,000 professional and technical personnel,” exemplifies the kind of expertise that can guide buyers through complex choices, such as selecting the right steel alloy or understanding the optimal processing techniques.
This technical support is invaluable, especially when dealing with specific requirements like weldability (e.g., “1020 vs 1025 Carbon Steel: Which is Better for Welding?”) or needing “3 Steel Alloys That Boost Strength and Reliability”. A knowledgeable supplier can also offer “Order Production” and “Processing Service” to meet customized demands, ensuring the high carbon steel billet or billet stainless steel is delivered precisely to specification. The “secret” here is that a superior product starts with a superior supplier who can not only provide the material but also the knowledge to use it effectively.
High Carbon Steel Billet vs Billet Stainless Steel: A Comparative Overview

To further clarify the differences, here is a comparative overview of high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel. This table distills the key attributes discussed, offering a quick reference for B2B buyers.
| Feature | High Carbon Steel Billet | Billet Stainless Steel |
| Defining Element | High Carbon Content (0.60% – 1.70%) | Minimum 10.5% Chromium Content |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional Hardness, High Strength, Wear Resistance (after heat treatment) | Superior Corrosion Resistance, Aesthetic Appeal, Hygiene |
| Corrosion Resistance | Poor; susceptible to rust without protective coatings | Excellent; forms a passive protective layer |
| Hardness | Very High (can be optimized via heat treatment) | Varies by grade; generally lower than high carbon steel, but can be hardened |
| Strength | High Tensile Strength | Varies by grade; good to excellent, can be high for some alloys like duplex or PH grades |
| Ductility | Lower; more brittle | Higher (especially austenitic grades); more formable |
| Weldability | Challenging; requires pre-heating and post-weld heat treatment to avoid cracking | Generally good to excellent; varies by grade, some grades require specific procedures |
| Typical Applications | Cutting tools, springs, dies, railway components, heavy machinery, wear-resistant parts | Food processing, medical instruments, marine applications, architecture, chemical plants |
| Cost (Initial) | Generally Lower | Generally Higher |
| Maintenance | Requires protective coatings, more susceptible to degradation in harsh environments | Lower maintenance due to inherent corrosion resistance, longer service life |
Further Considerations for high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel

Beyond the top three secrets, several other factors influence the choice between high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel. These often relate to specific manufacturing processes and logistical considerations.
Welding Challenges: High Carbon vs Stainless Billets The “welding challenge” is a significant differentiator. High carbon steel billet is notoriously difficult to weld due to its high carbon content, which increases its hardenability and susceptibility to cracking during the welding process. This often necessitates complex pre-heating and post-weld heat treatment procedures. In contrast, many grades of billet stainless steel, particularly austenitic types, offer excellent weldability, although specific grades may require specialized techniques to maintain corrosion resistance or prevent sensitization. This difference is critical for manufacturers where welding is a primary fabrication method. The news article “1020 vs 1025 Carbon Steel: Which is Better for Welding?” from our sources underlines this importance.
Precision Machining: The Machinability of Two Billets When it comes to “precision machining,” both high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel present unique challenges. High carbon steel billet, due to its hardness, can be difficult to machine, leading to increased tool wear. However, its consistent structure can allow for precise control if the right tools and cutting speeds are used. Billet stainless steel, particularly certain grades, can be prone to work hardening during machining, which can also complicate the process. Specialized machining techniques and coolants are often required to achieve the desired dimensional accuracy and surface finish for precision processed steel. Companies offering “Processing Service” can provide valuable insights and capabilities here.
Customization Needs: Tailoring Billets for Specific Projects “Customization needs” are increasingly common in B2B procurement. Whether you require a high carbon steel billet with specific heat treatment parameters or a unique grade of billet stainless steel for a specialized environment, the ability of a supplier to offer “Order Production” and “Processing Service” is invaluable. This ensures that the raw material, be it high carbon steel billet or billet stainless steel, is perfectly aligned with the project’s exact requirements, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Supply Chain Stability: Ensuring Long-Term Supply of Billets Finally, “supply chain stability” is a crucial operational concern. Establishing relationships with reputable and large-scale manufacturers like Henan Jiyuan Iron & Steel, with its substantial assets and employee base, ensures a consistent and reliable supply of both high carbon steel billet and billet stainless steel. This minimizes the risks of production delays and ensures continuous operations, which is a major concern for any B2B buyer.
Conclusion
The journey through the intricacies of high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel reveals that the “secret” to successful material selection lies in a deep understanding of their fundamental properties, application-specific requirements, and the unwavering commitment to quality. The choice between high carbon steel billet, prized for its hardness and strength, and billet stainless steel, renowned for its unparalleled corrosion resistance and versatility, is a strategic one that directly impacts product performance, durability, and overall project economics.
By understanding the three top secrets – the distinct performance differences, the alignment of material with application and cost, and the critical role of quality standards and supplier expertise – B2B buyers are empowered to make informed decisions. Companies like Henan Jiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Co., Ltd., with their long history, extensive technical personnel, and comprehensive services, stand as examples of partners who can provide not just high-quality steel billet but also the crucial support needed to navigate these complex choices. Ultimately, a well-chosen steel billet is not just a raw material; it is the foundation of quality, reliability, and success for your downstream products.
FAQ
Q1: What are the primary differences in heat treatment requirements for high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel?
A1: High carbon steel billet often undergoes extensive heat treatment (annealing, normalizing, hardening, tempering) to achieve specific hardness and strength properties. Billet stainless steel also undergoes heat treatment, but its primary goals might include stress relief, solution annealing to restore corrosion resistance, or precipitation hardening for specific grades, rather than just maximizing hardness.
Q2: Can high carbon steel billet be made corrosion-resistant?
A2: High carbon steel billet itself is not inherently corrosion-resistant. It can be made more resistant to corrosion through various surface treatments, such as plating, painting, or galvanizing. However, these are external coatings and do not provide the same intrinsic, self-healing corrosion resistance as billet stainless steel.
Q3: Which is more expensive, high carbon steel billet or billet stainless steel?
A3: Generally, billet stainless steel has a higher initial material cost due to the presence of expensive alloying elements like chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. High carbon steel billet is typically more affordable per unit weight. However, the total cost of ownership needs to consider factors like maintenance, lifespan, and performance in the intended environment.
Q4: How does Jiyuan Steel ensure the quality of its steel billet products?
A4: Jiyuan Steel emphasizes “Quality Steel Innovations” and provides “Inspection Services” to ensure product quality. With 3,000 professional and technical personnel, they likely employ stringent quality control measures, including chemical composition analysis, mechanical testing, and adherence to industry norms.
Q5: For a new product requiring both high strength and corrosion resistance, which billet should I choose?
A5: This is a classic dilemma in high carbon steel billet vs billet stainless steel selection. If both properties are critical, you might consider specific high-strength stainless steel grades (like duplex stainless steels or precipitation-hardening stainless steels) or explore high carbon steel billet with advanced surface protection. Consulting with a supplier’s “Tech Support” team, such as that offered by Jiyuan Steel, would be highly beneficial to weigh the trade-offs and find the optimal solution.






