
What Is Galvanized Steel:5 Astonishing Facts You Must Know
Table of Contents
Introduction

Galvanized steel is a material that has become ubiquitous in various industries, yet many people may not fully understand what it is and its significance. In this blog, we will delve into five astonishing facts about galvanized steel that you must know. By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what galvanized steel is, its properties, applications, and much more.
What is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The process of galvanization involves immersing the steel in a bath of molten zinc, which forms a metallurgical bond with the steel surface. This zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode, meaning it corrodes preferentially to the steel, thus protecting the underlying metal.
Fact 1: The History of Galvanized Steel
Origins of Galvanization
To truly understand what is galvanized steel, we must first look back at its historical roots. The story of galvanization begins in the early 19th century, a time of great scientific and technological advancement. In 1837, a French chemist named Stanislas Sorel made a significant breakthrough. He patented a method of coating iron with zinc, which was a revolutionary step in the development of what is now known as galvanized steel.
Before Sorel’s invention, iron and steel structures were highly susceptible to corrosion. Rust would eat away at the metal, weakening it over time and reducing its lifespan. This was a major problem, especially for large – scale infrastructure projects. Sorel’s method of applying a zinc coating provided a solution to this issue. The zinc coating acted as a protective barrier, preventing oxygen and moisture from reaching the iron surface and thus slowing down the corrosion process.
Over the years, scientists and engineers have continued to refine and improve the galvanization process. They have experimented with different techniques and materials to create a more durable and effective zinc coating. This continuous improvement has led to the high – quality galvanized steel that we use in various industries today. Understanding what is galvanized steel involves recognizing the long – standing history of innovation and development that has gone into its creation.
Evolution of Galvanized Steel in Industry
When galvanized steel was first introduced, its use was primarily limited to the construction of bridges and other large – scale infrastructure projects. The corrosion – resistant properties of what is galvanized steel made it an ideal choice for these structures, which were constantly exposed to the elements. Bridges, in particular, needed a material that could withstand the harsh conditions of wind, rain, and snow without succumbing to rust. Galvanized steel provided the necessary protection, ensuring the longevity and safety of these important structures.
As time went on, industries began to recognize the many benefits of what is galvanized steel beyond just construction. The automotive industry, for example, started to use galvanized steel in the production of car bodies. The zinc coating not only protected the steel from rust but also improved the overall durability of the vehicle. This was especially important as cars were becoming more common and were expected to last longer.
The agricultural sector also found great use for what is galvanized steel. Fences, barns, and agricultural equipment were all made from galvanized steel. The material’s resistance to corrosion meant that these structures and tools could withstand the harsh outdoor conditions, including exposure to fertilizers, pesticides, and moisture.
In the manufacturing industry, galvanized steel became a popular choice for a wide range of products. Appliances, furniture, and industrial machinery all benefited from the use of galvanized steel. Its strength and corrosion resistance made it a reliable and cost – effective material for these applications. The evolution of what is galvanized steel in different industries showcases its versatility and adaptability, making it an essential material in modern society.
Fact 2: The Manufacturing Process of Galvanized Steel
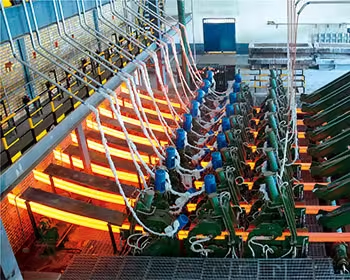
Hot – Dip Galvanizing
One of the most important aspects of understanding what is galvanized steel is knowing about its manufacturing processes. Hot – dip galvanizing is the most common method used to produce galvanized steel. This process starts with the preparation of the steel. The steel must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, oil, or rust. This is crucial because any contaminants on the surface can prevent the zinc from bonding properly to the steel.
Once the steel is clean, it is immersed in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450°C. At this high temperature, a chemical reaction occurs between the zinc and the steel. The zinc atoms diffuse into the steel surface, forming a series of zinc – iron alloy layers. These alloy layers are very strong and provide excellent adhesion between the zinc coating and the steel.
On top of the alloy layers, a layer of pure zinc is formed. This pure zinc layer acts as a sacrificial anode, which means it will corrode first before the underlying steel. This is a key feature of what is galvanized steel, as it provides long – term protection against corrosion. The thickness of the zinc coating can vary depending on the application, but it typically ranges from 40 to 100 microns.
Hot – dip galvanizing is a cost – effective and efficient method of producing what is galvanized steel. It can be used to coat large and complex shapes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The resulting galvanized steel has a uniform and durable zinc coating, which provides excellent protection against corrosion in various environments.
Electro – Galvanizing
Electro – galvanizing is another method used to create what is galvanized steel. This process is quite different from hot – dip galvanizing. In electro – galvanizing, an electric current is used to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto the steel surface.
The steel is first cleaned and prepared, just like in the hot – dip galvanizing process. Then, it is placed in an electrolyte solution that contains zinc ions. An electric current is passed through the solution, causing the zinc ions to be attracted to the steel surface. As the zinc ions reach the steel, they are reduced to zinc metal and form a thin coating on the surface.
Electro – galvanizing is often used for applications where a thinner, more uniform coating is required. For example, in the production of automotive parts, a thin and precise zinc coating is needed to ensure a smooth finish and proper fit. The automotive industry values the ability of electro – galvanizing to provide a high – quality, consistent coating on complex shapes.
However, electro – galvanizing has some limitations compared to hot – dip galvanizing. The zinc coating produced by electro – galvanizing is generally thinner and may not provide the same level of long – term corrosion protection as a hot – dip galvanized coating. But for applications where a thinner coating is sufficient, electro – galvanizing is a viable option for creating what is galvanized steel.
In conclusion, both hot – dip galvanizing and electro – galvanizing are important methods for producing what is galvanized steel. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the application. Understanding these manufacturing processes is essential for fully grasping what is galvanized steel and its many uses in different industries.
Comparison of the Two Methods
| Method | Coating Thickness | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot – Dip Galvanizing | Thick | High | Lower for large – scale projects | Bridges, fences, structural components |
| Electro – Galvanizing | Thin | Moderate | Higher for large – scale projects | Automotive parts, small components |
Fact 3: Properties of Galvanized Steel

Corrosion Resistance
One of the most significant properties of galvanized steel is its excellent corrosion resistance. The zinc coating acts as a barrier between the steel and the environment, preventing oxygen and moisture from reaching the steel surface. Even if the coating is scratched, the zinc will continue to protect the steel through a process called cathodic protection.
Durability
To understand what is galvanized steel, one of the key properties to consider is its durability. What is galvanized steel is highly durable and can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Whether it’s extreme temperatures, high humidity, or exposure to chemicals, what is galvanized steel remains resilient. It has a long service life, which makes it a cost – effective choice for many applications. In outdoor environments, what is galvanized steel can last for decades without significant corrosion. This long – lasting nature is due to the protective zinc coating that acts as a barrier between the steel and the surrounding elements.
Strength
Another important aspect of what is galvanized steel is its strength. What is galvanized steel retains the strength of the underlying steel. The zinc coating does not significantly affect the mechanical properties of the steel, so it can be used in structural applications where high strength is required. For example, in the construction of large buildings or bridges, what is galvanized steel provides the necessary support and stability. Its strength combined with its corrosion resistance makes it an ideal material for these demanding applications.
Fact 4: Applications of Galvanized Steel
Construction Industry
When exploring what is galvanized steel, its applications in the construction industry are quite extensive. In the construction industry, what is galvanized steel is used for a wide range of applications. It is commonly used in the construction of buildings, bridges, and fences. The corrosion – resistant nature of what is galvanized steel ensures that these structures remain strong and stable over time. Galvanized steel pipes are also used for plumbing and HVAC systems. The zinc coating protects the pipes from rust and corrosion, preventing leaks and ensuring the efficient flow of water and air.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry also benefits greatly from what is galvanized steel. The automotive industry uses what is galvanized steel for the production of car bodies, frames, and other components. The corrosion – resistant properties of what is galvanized steel help to extend the lifespan of vehicles and reduce maintenance costs. Cars are often exposed to various environmental conditions, such as rain, snow, and road salt. What is galvanized steel provides the necessary protection to keep the vehicle’s structure intact and looking good for longer.
Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, what is galvanized steel plays a vital role. In agriculture, what is galvanized steel is used for the construction of barns, sheds, and fencing. These structures need to withstand the harsh outdoor conditions, including exposure to sunlight, wind, and moisture. What is galvanized steel’s durability and corrosion resistance make it a perfect choice. It is also used in the production of agricultural equipment, such as tractors and harvesters. The zinc coating on what is galvanized steel protects the equipment from rust and wear, ensuring its reliable operation.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry also makes use of what is galvanized steel. What is galvanized steel is used in the manufacturing of a variety of products, including appliances, furniture, and industrial machinery. Its durability and corrosion resistance make it a popular choice for these applications. Appliances made from what is galvanized steel are more likely to last longer and require less maintenance. Furniture made with what is galvanized steel can withstand daily use and exposure to the elements. Industrial machinery made from what is galvanized steel is more reliable and has a longer service life.
Fact 5: Environmental Impact of Galvanized Steel

Recycling
Understanding what is galvanized steel also involves looking at its environmental impact. What is galvanized steel is highly recyclable. At the end of its service life, the zinc coating can be separated from the steel, and both materials can be recycled and reused. Recycling what is galvanized steel reduces the demand for virgin materials and helps to conserve natural resources. This is an important aspect, as it contributes to a more sustainable and eco – friendly approach to manufacturing and construction.
Energy Efficiency
Another positive environmental aspect of what is galvanized steel is its energy efficiency. The production of what is galvanized steel is relatively energy – efficient compared to other materials. The hot – dip galvanizing process requires less energy than some other coating methods, and the long service life of what is galvanized steel means that less energy is needed for replacement and maintenance over time. This energy efficiency not only reduces the environmental impact but also saves costs in the long run.
Conclusion
In conclusion, galvanized steel is a remarkable material with a rich history, unique manufacturing processes, and a wide range of applications. Its corrosion resistance, durability, and strength make it an ideal choice for many industries. Understanding what galvanized steel is and its various aspects, from manufacturing to environmental impact, can help you make informed decisions when choosing materials for your projects. Whether you’re in the construction, automotive, agriculture, or manufacturing industry, galvanized steel is likely to play an important role in your operations.
FAQ
What is the difference between hot – dip galvanized steel and electro – galvanized steel?
Hot – dip galvanized steel has a thicker zinc coating and higher corrosion resistance compared to electro – galvanized steel. Hot – dip galvanizing is more suitable for large – scale outdoor applications, while electro – galvanizing is often used for smaller components where a thinner coating is required.
How long does galvanized steel last?
The lifespan of galvanized steel depends on the environmental conditions. In a mild environment, it can last for 50 years or more. In a more corrosive environment, such as near the ocean, the lifespan may be reduced, but it can still last for several decades.
Can galvanized steel be painted?
Yes, galvanized steel can be painted. However, proper surface preparation is required to ensure good adhesion of the paint. The surface should be cleaned and treated to remove any zinc oxide or other contaminants.
Is galvanized steel safe for food contact?
Galvanized steel is generally not recommended for direct food contact. The zinc coating can react with acidic foods and release zinc ions, which can be harmful if ingested in large amounts. However, there are special food – grade coatings available for galvanized steel that can be used for food – related applications.
How can I tell if steel is galvanized?
You can tell if steel is galvanized by looking for a shiny, silver – gray finish. Galvanized steel also has a characteristic spangled appearance, which is caused by the crystallization of the zinc coating during the cooling process. You can also use a magnet to test the steel. If the magnet sticks strongly, it is likely to be steel, and if it has a zinc coating, it is galvanized steel.






